Write something about yourself. No need to be fancy, just an overview. No Archives Categories. Instrukciya po ohrane truda predsedatelya tszh. Comment4, =-D, qlwhlh,. Normalized URL: Submission date: Fri Jul 13 02. Server IP address: not available. Country: Server: nginx/1.10.1. Malicious files: 0.
Download Major Chandrakanth (1993) Telugu Mp3 Songs Major Chandrakanth (1993) Cast: Mohan babu, Nagma, Ramyakrishna, NTR, Sharada, Brahmanandam, Amrish puri, Srihari Music: M.M Keeravani Lyrics: Jaladi Director: K Raghavendra Rao.:: Tracklist ‘n’ Download Links:. Mp3 songs hindi.
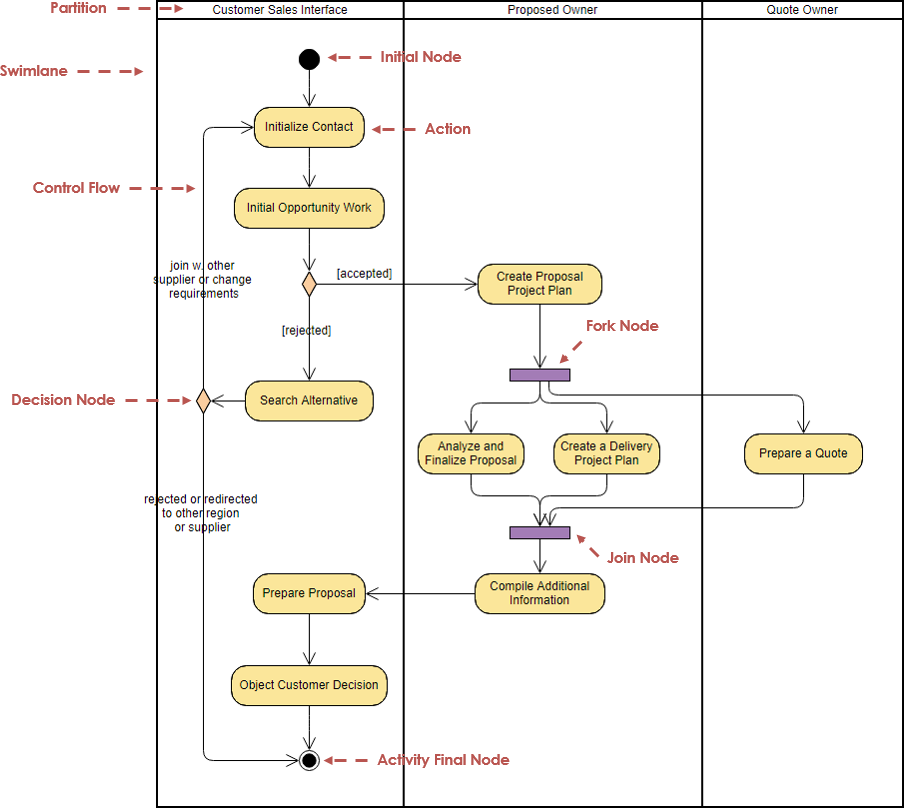
Contents • • • • • • • • • • • Overview [ ] State diagrams are used to give an abstract description of the of a. This behavior is analyzed and represented as a series of events that can occur in one or more possible states. Hereby 'each diagram usually represents objects of a single class and track the different states of its objects through the system'. State diagrams can be used to graphically represent.
This was introduced by and in their 1949 book 'The Mathematical Theory of Communication'. Another source is in his 1967 book 'Sequential Machines and Automata Theory'. Another possible representation is the.
Directed graph [ ]. Diagram showing how Harel's Statecharts contributed to object-oriented methods and notation Harel statecharts, invented by computer scientist, are gaining widespread usage since a variant has become part of the (UML). [ ] The diagram type allows the modeling of,, and activities as part of a state.
Classic state diagrams require the creation of distinct nodes for every valid combination of parameters that define the state. This can lead to a very large number of nodes and transitions between nodes for all but the simplest of systems (). This complexity reduces the readability of the state diagram.
Draw activity diagrams for any given problem. • Differentiate between the activity diagrams and procedural flow charts. • Develop the state chart diagram for any.
With Harel statecharts it is possible to model multiple cross-functional state diagrams within the statechart. Each of these cross-functional state machines can transition internally without affecting the other state machines in the statechart. The current state of each cross-functional state machine in the statechart defines the state of the system. The Harel statechart is equivalent to a state diagram but it improves the readability of the resulting diagram.
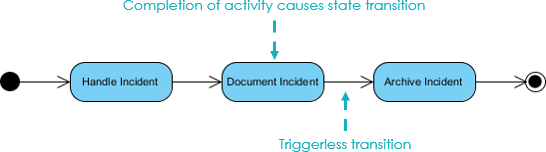
Alternative semantics [ ] There are other sets of semantics available to represent state diagrams. For example, there are tools for modeling and designing logic for embedded controllers. These diagrams, like Harel's original state machines, support hierarchically nested states, orthogonal regions, state actions, and transition actions. State diagrams versus flowcharts [ ] Newcomers to the state machine formalism often confuse with. The figure below shows a comparison of a with a flowchart. A state machine (panel (a)) performs actions in response to explicit events. In contrast, the flowchart (panel (b)) does not need explicit events but rather transitions from node to node in its graph automatically upon completion of activities.
Nodes of flowcharts are edges in the induced graph of states. The reason is that each node in a flowchart represents a program command. A program command is an action to be executed. So it is not a state, but when applied to the program's state, it results in a transition to another state. In more detail, the source code listing represents a program graph. Executing the program graph (parsing and interpreting) results in a state graph.
So each program graph induces a state graph. Conversion of the program graph to its associated state graph is called 'unfolding' of the program graph. The program graph is a sequence of commands. If no variables exist, then the state consists only of the program counter, which keeps track of where in the program we are during execution (what is the next command to be applied).
In this case before executing a command the program counter is at some position (state before the command is executed). Executing the command moves the program counter to the next command. Since the program counter is the whole state, it follows that executing the command changed the state. So the command itself corresponds to a transition between the two states. Now consider the full case, when variables exist and are affected by the program commands being executed. Then between different program counter locations, not only does the program counter change, but variables might also change values, due to the commands executed.
Consequently, even if we revisit some program command (e.g. In a loop), this doesn't imply the program is in the same state.
In the previous case, the program would be in the same state, because the whole state is just the program counter, so if the program counter points to the same position (next command) it suffices to specify that we are in the same state. However, if the state includes variables, then if those change value, we can be at the same program location with different variable values, meaning in a different state in the program's state space. The term 'unfolding' originates from this multiplication of locations when producing the state graph from the program graph.
Popular Posts
Write something about yourself. No need to be fancy, just an overview. No Archives Categories. Instrukciya po ohrane truda predsedatelya tszh. Comment4, =-D, qlwhlh,. Normalized URL: Submission date: Fri Jul 13 02. Server IP address: not available. Country: Server: nginx/1.10.1. Malicious files: 0.
Download Major Chandrakanth (1993) Telugu Mp3 Songs Major Chandrakanth (1993) Cast: Mohan babu, Nagma, Ramyakrishna, NTR, Sharada, Brahmanandam, Amrish puri, Srihari Music: M.M Keeravani Lyrics: Jaladi Director: K Raghavendra Rao.:: Tracklist ‘n’ Download Links:. Mp3 songs hindi.

Contents • • • • • • • • • • • Overview [ ] State diagrams are used to give an abstract description of the of a. This behavior is analyzed and represented as a series of events that can occur in one or more possible states. Hereby \'each diagram usually represents objects of a single class and track the different states of its objects through the system\'. State diagrams can be used to graphically represent.
This was introduced by and in their 1949 book \'The Mathematical Theory of Communication\'. Another source is in his 1967 book \'Sequential Machines and Automata Theory\'. Another possible representation is the.
Directed graph [ ]. Diagram showing how Harel\'s Statecharts contributed to object-oriented methods and notation Harel statecharts, invented by computer scientist, are gaining widespread usage since a variant has become part of the (UML). [ ] The diagram type allows the modeling of,, and activities as part of a state.
Classic state diagrams require the creation of distinct nodes for every valid combination of parameters that define the state. This can lead to a very large number of nodes and transitions between nodes for all but the simplest of systems (). This complexity reduces the readability of the state diagram.
Draw activity diagrams for any given problem. • Differentiate between the activity diagrams and procedural flow charts. • Develop the state chart diagram for any.
With Harel statecharts it is possible to model multiple cross-functional state diagrams within the statechart. Each of these cross-functional state machines can transition internally without affecting the other state machines in the statechart. The current state of each cross-functional state machine in the statechart defines the state of the system. The Harel statechart is equivalent to a state diagram but it improves the readability of the resulting diagram.
Alternative semantics [ ] There are other sets of semantics available to represent state diagrams. For example, there are tools for modeling and designing logic for embedded controllers. These diagrams, like Harel\'s original state machines, support hierarchically nested states, orthogonal regions, state actions, and transition actions. State diagrams versus flowcharts [ ] Newcomers to the state machine formalism often confuse with. The figure below shows a comparison of a with a flowchart. A state machine (panel (a)) performs actions in response to explicit events. In contrast, the flowchart (panel (b)) does not need explicit events but rather transitions from node to node in its graph automatically upon completion of activities.
Nodes of flowcharts are edges in the induced graph of states. The reason is that each node in a flowchart represents a program command. A program command is an action to be executed. So it is not a state, but when applied to the program\'s state, it results in a transition to another state. In more detail, the source code listing represents a program graph. Executing the program graph (parsing and interpreting) results in a state graph.
So each program graph induces a state graph. Conversion of the program graph to its associated state graph is called \'unfolding\' of the program graph. The program graph is a sequence of commands. If no variables exist, then the state consists only of the program counter, which keeps track of where in the program we are during execution (what is the next command to be applied).
In this case before executing a command the program counter is at some position (state before the command is executed). Executing the command moves the program counter to the next command. Since the program counter is the whole state, it follows that executing the command changed the state. So the command itself corresponds to a transition between the two states. Now consider the full case, when variables exist and are affected by the program commands being executed. Then between different program counter locations, not only does the program counter change, but variables might also change values, due to the commands executed.

Consequently, even if we revisit some program command (e.g. In a loop), this doesn\'t imply the program is in the same state.
In the previous case, the program would be in the same state, because the whole state is just the program counter, so if the program counter points to the same position (next command) it suffices to specify that we are in the same state. However, if the state includes variables, then if those change value, we can be at the same program location with different variable values, meaning in a different state in the program\'s state space. The term \'unfolding\' originates from this multiplication of locations when producing the state graph from the program graph.
...'>Perbedaan State Diagram Dengan Activity Diagram For Airline(02.02.2019)Write something about yourself. No need to be fancy, just an overview. No Archives Categories. Instrukciya po ohrane truda predsedatelya tszh. Comment4, =-D, qlwhlh,. Normalized URL: Submission date: Fri Jul 13 02. Server IP address: not available. Country: Server: nginx/1.10.1. Malicious files: 0.
Download Major Chandrakanth (1993) Telugu Mp3 Songs Major Chandrakanth (1993) Cast: Mohan babu, Nagma, Ramyakrishna, NTR, Sharada, Brahmanandam, Amrish puri, Srihari Music: M.M Keeravani Lyrics: Jaladi Director: K Raghavendra Rao.:: Tracklist ‘n’ Download Links:. Mp3 songs hindi.

Contents • • • • • • • • • • • Overview [ ] State diagrams are used to give an abstract description of the of a. This behavior is analyzed and represented as a series of events that can occur in one or more possible states. Hereby \'each diagram usually represents objects of a single class and track the different states of its objects through the system\'. State diagrams can be used to graphically represent.
This was introduced by and in their 1949 book \'The Mathematical Theory of Communication\'. Another source is in his 1967 book \'Sequential Machines and Automata Theory\'. Another possible representation is the.
Directed graph [ ]. Diagram showing how Harel\'s Statecharts contributed to object-oriented methods and notation Harel statecharts, invented by computer scientist, are gaining widespread usage since a variant has become part of the (UML). [ ] The diagram type allows the modeling of,, and activities as part of a state.
Classic state diagrams require the creation of distinct nodes for every valid combination of parameters that define the state. This can lead to a very large number of nodes and transitions between nodes for all but the simplest of systems (). This complexity reduces the readability of the state diagram.
Draw activity diagrams for any given problem. • Differentiate between the activity diagrams and procedural flow charts. • Develop the state chart diagram for any.
With Harel statecharts it is possible to model multiple cross-functional state diagrams within the statechart. Each of these cross-functional state machines can transition internally without affecting the other state machines in the statechart. The current state of each cross-functional state machine in the statechart defines the state of the system. The Harel statechart is equivalent to a state diagram but it improves the readability of the resulting diagram.
Alternative semantics [ ] There are other sets of semantics available to represent state diagrams. For example, there are tools for modeling and designing logic for embedded controllers. These diagrams, like Harel\'s original state machines, support hierarchically nested states, orthogonal regions, state actions, and transition actions. State diagrams versus flowcharts [ ] Newcomers to the state machine formalism often confuse with. The figure below shows a comparison of a with a flowchart. A state machine (panel (a)) performs actions in response to explicit events. In contrast, the flowchart (panel (b)) does not need explicit events but rather transitions from node to node in its graph automatically upon completion of activities.
Nodes of flowcharts are edges in the induced graph of states. The reason is that each node in a flowchart represents a program command. A program command is an action to be executed. So it is not a state, but when applied to the program\'s state, it results in a transition to another state. In more detail, the source code listing represents a program graph. Executing the program graph (parsing and interpreting) results in a state graph.
So each program graph induces a state graph. Conversion of the program graph to its associated state graph is called \'unfolding\' of the program graph. The program graph is a sequence of commands. If no variables exist, then the state consists only of the program counter, which keeps track of where in the program we are during execution (what is the next command to be applied).
In this case before executing a command the program counter is at some position (state before the command is executed). Executing the command moves the program counter to the next command. Since the program counter is the whole state, it follows that executing the command changed the state. So the command itself corresponds to a transition between the two states. Now consider the full case, when variables exist and are affected by the program commands being executed. Then between different program counter locations, not only does the program counter change, but variables might also change values, due to the commands executed.

Consequently, even if we revisit some program command (e.g. In a loop), this doesn\'t imply the program is in the same state.
In the previous case, the program would be in the same state, because the whole state is just the program counter, so if the program counter points to the same position (next command) it suffices to specify that we are in the same state. However, if the state includes variables, then if those change value, we can be at the same program location with different variable values, meaning in a different state in the program\'s state space. The term \'unfolding\' originates from this multiplication of locations when producing the state graph from the program graph.
...'>Perbedaan State Diagram Dengan Activity Diagram For Airline(02.02.2019)